Are electric vehicle chargers universal remains a nuanced question. While standard Level 1 EV charger and Level 2 EV charger systems offer broad compatibility, fast charging and proprietary connectors limit full universality. Knowing EV connector types explained and following EV charging standards ensures vehicles charge safely and efficiently. For international travel or public networks, using an EV adapter for charging and referencing EV charging compatibility charts helps maintain consistent performance. Understanding these distinctions allows EV owners to plan effectively, avoid errors, and achieve optimal electric car charging speed across diverse charging environments.
Understanding the Question Are Electric Vehicle Chargers Universal?
Many EV owners often ask Are EV chargers universal, especially when considering home or public charging. Understanding EV charger compatibility is essential because not all vehicles accept the same charging method. While a Level 1 EV charger works with most cars at home, Level 2 EV charger setups and DC fast charging stations may require specific connectors or adapters. Questions like Do all electric cars use the same charger arise due to varying EV plug types and regional standards. Proprietary designs like the Tesla NACS port can complicate compatibility, making EV adapter for charging necessary. Users must understand EV charging standards to avoid damage and ensure safety. Even within public stations, different EV charging infrastructure may offer multiple plug options, which impacts how quickly and safely a car charges. A simple mismatch can lead to inefficiency or even risk to the battery.
Understanding electric car charging speed and station compatibility is crucial for travel planning. While a Level 1 EV charger provides slow overnight charging, fast EV charging through DC fast charging stationsIs critical for lengthy trips. International travelers face added complexity, as EV charging in different countries may require unique adapters or plugs. Using an EV charging compatibility chart can clarify which chargers match your vehicle. Knowing EV charger types and EV charging port variations ensures safe operation and reduces downtime. Users often wonder Can I use any charger for my EV, but the answer depends on standards and connector types. Awareness of EV charging safety standards protects both the vehicle and the user. Ultimately, knowing these fundamentals helps answer the critical question, Are EV chargers universal?
Are Electric Vehicle Chargers Universal
Are electric vehicle chargers universal remains a nuanced question. While standard Level 1 EV charger and Level 2 EV charger systems offer broad compatibility, fast charging and proprietary connectors limit full universality. Knowing EV connector types explained and following EV charging standards ensures vehicles charge safely and efficiently. For international travel or public networks, using an EV adapter for charging and referencing EV charging compatibility charts helps maintain consistent performance. Understanding these distinctions allows EV owners to plan effectively, avoid errors, and achieve optimal electric car charging speed across diverse charging environments.
EV Charger Levels and Compatibility Comparison
| Charger Type | Voltage Range | Charging Speed | Common Connectors | Compatibility | Best Application |
| Level 1 | 120V (AC) | Slow charging (8–12 hours for full charge) | J1772 | Highly universal for most EVs | Ideal for home overnight charging |
| Level 2 | 240V (AC) | Moderate charging (4–6 hours for full charge) | J1772 / Type 2 | Broadly compatible across brands | Home or public stations |
| Level 3 (DC Fast) | 400–900V (DC) | Very fast charging (30–60 minutes) | CCS / CHAdeMO / NACS | Brand and region-specific | Best for highway or long-distance travel |
The table shows that Level 1 and Level 2 chargers are mostly universal, while Level 3 or DC fast chargers depend heavily on the connector type and region. This highlights why electric vehicle charger universality remains limited despite growing global standardization efforts.
What Does “Universal” Mean in EV Charging Context?
The term universal in EV charging refers to a system that works across multiple vehicle brands without modification. A true Universal EV plug would allow any car to charge at any station safely. However, Why EV chargers are not universal is explained by varying EV charging standards. Differences between Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 chargers affect compatibility, as each level has unique power ratings and connector types. Some vehicles use CHAdeMO connector, others follow CCS charging standard, and Tesla uses Tesla NACS port. Public stations may provide multiple connectors, but often an EV adapter for charging is required. Knowing EV connector types explained helps users choose the correct charger. Misusing a charger can slow electric car charging speed or even damage the battery. A Universal EV plug remains an ideal, but current infrastructure and brand differences limit its reality.
Even in home setups, not all EV home charger units support multiple brands. Users often ask What type of charger does my EV need, highlighting the importance of understanding EV plug types. Comparing Tesla charging vs other EVs demonstrates how proprietary systems complicate universality. Fast charging compatibility matters for long trips, while adapters and knowledge of EV charging station types help overcome limitations. Users should also consider EV charging in different countries, as international plugs vary. Following how to check EV charger compatibility ensures vehicles charge efficiently and safely. Understanding AC vs DC EV charging further clarifies power differences. Awareness of Universal EV charger myths protects against misinformation and prepares users for real-world conditions.
The Three Levels of EV Charging Explained (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3)
Understanding differences between Level 1, Level 2, Level 3 chargers is essential when asking Are EV chargers universal. A Level 1 EV charger connects to a standard household outlet, providing slow but steady charging, ideal for overnight use. Most EVs accept this method without additional equipment, which demonstrates basic EV charger compatibility. Level 2 EV charger systems require higher voltage and deliver faster energy transfer, commonly installed at homes or public parking areas. Users often ask Can I use any charger for my EV, but Level 2 may need specific wiring or connectors. DC fast charging stations supply high voltage directly to the battery, dramatically reducing charging time, but they are often brand-specific or region-specific. EV plug types vary, and proprietary systems like Tesla NACS port or CHAdeMO connector limit universality. Using an EV adapter for charging can solve some compatibility problems but requires careful selection.
Electric car charging speed depends heavily on the charger level and vehicle battery. Fast EV charging allows long-distance travel, while Level 1 suits daily commuting. EV charging infrastructure in urban areas increasingly supports multiple connectors, but international travelers must check EV charging in different countries for differences in voltage or plug type. Public stations often offer EV charging station types that combine Level 2 and DC fast options. Tools like an EV charging compatibility chart help drivers choose the right option, reducing risk of downtime or battery stress. Understanding AC vs DC EV charging further informs decisions. Knowing what type of charger does my EV need ensures safe operation and prevents unnecessary damage. Questions like Do all electric cars use the same charger or Universal EV charger myths highlight common misconceptions. Clear knowledge of charger levels solves practical issues for all EV owners.
Why Level 1 and Level 2 Chargers Are Largely Compatible
Most home chargers are Level 1 EV charger or Level 2 EV charger, which makes them largely compatible across different EVs. EV charger compatibility is high because these chargers follow standardized power and connector specifications. Users frequently wonder Can I use any charger for my EV, and in most home scenarios, the answer is yes. Level 1 chargers draw minimal current and plug into a household outlet, making them ideal for daily overnight charging. Level 2 chargers provide faster energy transfer but still comply with common EV charging standards, which increases their universality. Awareness of EV charging port types ensures the right connection. EV adapter for charging may be needed for older models, but generally, Level 1 and 2 provide seamless use. This explains why many EV owners report straightforward charging experiences at home.
Even public EV home charger installations maintain high compatibility, allowing multiple brands to use the same station. While DC fast charging varies in universality, Level 2 remains reliable. Understanding EV plug types and EV connector types explained allows users to avoid mistakes. Checking EV charging compatibility chart before purchasing or installing a charger ensures proper match. Electric car charging speed varies between Level 1 and Level 2, but both meet everyday driving needs. The integration of EV charging infrastructure and public networks continues to expand, offering more Level 2 options. Knowledge of Fast charging compatibility and EV charging safety standards enhances confidence for all drivers. This solid foundation addresses why Are EV chargers universal has a positive answer in home and most public Level 2 setups.
The Role of Connector Standards: J1772, Type 2, etc.
Connector standards are the backbone of EV charger compatibility and directly affect whether Are EV chargers universal is possible. The J1772 connector is widely used in North America for Level 1 EV charger and Level 2 EV charger setups, allowing multiple brands to plug in without modification. In Europe, the Type 2 connector dominates, offering similar universality. Despite these standardizations, proprietary plugs like Tesla NACS port or CHAdeMO connector exist, limiting full universality. Drivers often ask Do all electric cars use the same charger, and the answer depends heavily on these connector standards. An EV adapter for charging may resolve compatibility gaps, but understanding EV plug types beforehand ensures safe and efficient charging. EV charging infrastructure in public areas usually supports multiple standards to accommodate diverse vehicles.
Standardized connectors also impact fast EV charging and DC fast charging efficiency. Public stations often combine multiple EV charging station types to serve various vehicles, from Level 2 chargers to high-powered DC options. Knowing EV charging in different countries is important because connector standards differ internationally, affecting travelers. Checking an EV charging compatibility chart provides clarity on which vehicles match specific stations. Awareness of AC vs DC EV charging clarifies energy flow and compatibility. Electric car charging speed depends on both connector type and charger level. Users must also consider EV charging safety standards to avoid accidents. Proper knowledge of these standards answers practical questions like Can I use any charger for my EV and explains why Universal EV plug ideals are not fully realized yet.
DC Fast Charging Complexity: Why Level 3 Isn’t Fully Universal
DC fast charging allows electric vehicles to recharge rapidly, often in under an hour, making it essential for long-distance travel. However, Are EV chargers universal does not fully apply here. Unlike Level 1 EV charger and Level 2 EV charger, DC fast chargers rely on different connectors and higher voltage standards. Popular connectors like CHAdeMO connector and CCS charging standard create compatibility challenges. Tesla vehicles use Tesla NACS port, requiring either proprietary stations or adapters. Drivers often ask Do all electric cars use the same charger, but fast charging demonstrates why a single solution is impossible. Public EV charging infrastructure sometimes combines multiple DC plugs, yet not all stations cover every standard. Checking an EV charging compatibility chart ensures correct use and prevents damage.
Understanding fast EV charging is critical for planning trips. The electric car charging speed varies significantly based on battery size, charger power, and connector type. Users should learn EV connector types explained and use an EV adapter guide if necessary. Differences in EV charging in different countries make it important for international travelers to verify local DC standards. Observing EV charging safety standards during high-power charging prevents accidents. Knowledge of AC vs DC EV charging clarifies why universality fails for Level 3 setups. Realistic expectations about Universal EV plug availability and compatibility help drivers plan efficiently, ensuring their vehicle charges safely and quickly.
Major Connector Types for DC Fast: CHAdeMO, CCS, NACS
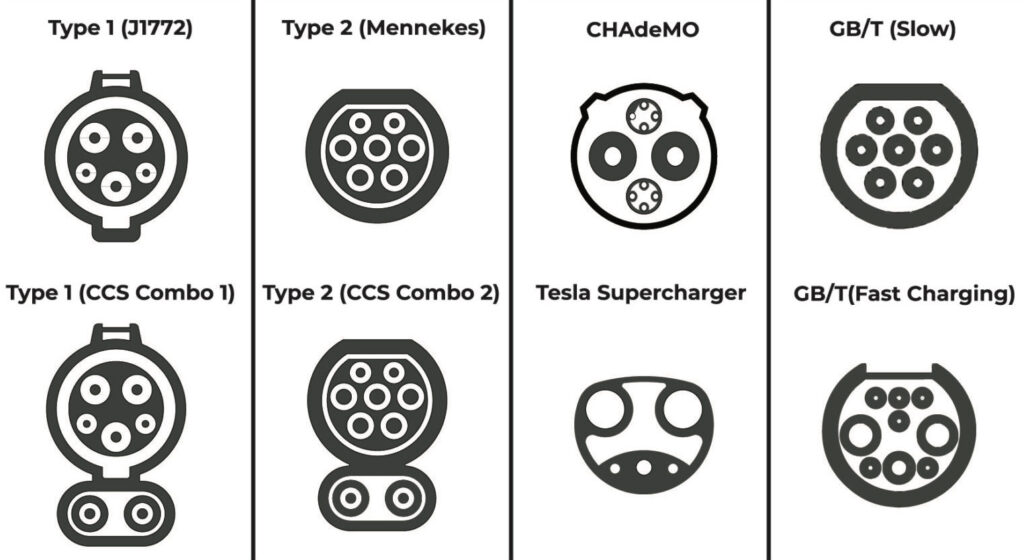
Understanding EV plug types is vital when considering Are EV chargers universal. The most common DC connectors include CHAdeMO connector, popular in Japanese EVs, CCS charging standard used in Europe and North America, and Tesla’s proprietary Tesla NACS port. Each type has unique pins and communication protocols, meaning a vehicle cannot use a different type without an EV adapter for charging. Many drivers ask Can I use any charger for my EV, but DC fast charging demonstrates why adapters or proprietary stations are often required. Knowledge of EV charging standards is crucial to ensure EV charger compatibility. Fast EV charging depends not only on connector type but also on voltage and current ratings.
Public EV charging infrastructure frequently includes stations supporting multiple connector types, increasing versatility. Checking an EV charging compatibility chart before travel is wise, especially for international trips, where EV charging in different countries may use uncommon connectors. EV charging station types vary from slow Level 2 to high-powered DC fast stations, affecting electric car charging speed. Users comparing Tesla charging vs other EVs find that proprietary systems limit access to universal DC chargers. Observing EV charging safety standards while connecting ensures safe and efficient operation. Understanding these connectors is essential for EV owners who need Best EV charger for multiple brands and smooth long-distance travel.
Regional Standards and Their Impact on Charger Compatibility
Regional standards heavily influence EV charger compatibility, which explains why Are EV chargers universal cannot be guaranteed. North America relies mainly on J1772 connector for Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, while Europe uses Type 2 plugs. DC fast chargers include CCS charging standard and CHAdeMO connector, but availability varies by country. EV charging in different countries may require travelers to adapt to local infrastructure. Many users ask Do all electric cars use the same charger, but voltage, plug, and communication protocols differ globally. Using an EV adapter for charging helps mitigate incompatibility, while EV charging compatibility chart provides clarity. Understanding AC vs DC EV charging helps predict charging time.
Local EV charging infrastructure impacts electric car charging speed and convenience. Public stations often provide EV charging station types to serve multiple brands, yet fast chargers remain brand-specific in many regions. Awareness of EV connector types explained and EV charging safety standards ensures proper and secure use. Home chargers like Level 2 EV charger units are largely universal, but proprietary systems like Tesla NACS port restrict global compatibility. Learning What type of charger does my EV need and checking for Fast charging compatibility allows drivers to plan journeys effectively. Knowledge of Universal EV plug ideals helps set realistic expectations.
Brand & Manufacturer Differences Proprietary Plugs and Networks
Vehicle manufacturers often create proprietary systems that limit EV charger compatibility, showing why Are EV chargers universal is a complex question. Tesla uses Tesla NACS port, while Japanese brands rely on CHAdeMO connector and European vehicles prefer CCS charging standard. Public EV charging infrastructure may not support all brands equally. Drivers frequently ask Can I use any charger for my EV, but proprietary plugs prevent full universality. EV charging standards aim to normalize plugs, yet fast chargers remain mostly brand-specific. Using an EV adapter for charging is sometimes required to bridge differences. Knowledge of EV plug types ensures safe and efficient connection.
Brand differences also affect fast EV charging. Comparing Tesla charging vs other EVs shows proprietary networks limit access to universal stations. Home setups with Level 1 EV charger or Level 2 EV charger are mostly universal, but public EV charging station types vary. Awareness of EV charging in different countries, electric car charging speed, and EV charging safety standards prevents misuse. EV charging compatibility chart helps determine which vehicles match each station. Choosing Best EV charger for multiple brands requires understanding manufacturer restrictions. Recognizing brand-specific barriers ensures drivers plan properly and avoid compatibility issues.
Adapter Solutions When & Why You Might Need One
Adapters play a crucial role in EV charger compatibility, especially when Are EV chargers universal is in question. Many vehicles use proprietary plugs such as the Tesla NACS port or the CHAdeMO connector, making direct charging impossible at some stations. An EV adapter for charging allows a vehicle to connect safely to Level 2 EV charger or DC fast charging stations. Drivers often ask Can I use any charger for my EV, and the answer is yes, but only with the correct adapter. Using an adapter ensures proper communication between the car and the charger, prevents overloading, and maintains electric car charging speed. Checking an EV charging compatibility chart helps select the right adapter for different brands and connector types.
Adapters also support international travel. EV charging in different countries often requires region-specific solutions. Awareness of EV plug types, EV connector types explained, and EV charging safety standards ensures adapters function correctly. Public EV charging station types sometimes provide built-in adapter options, but a personal adapter offers flexibility. Knowing What type of charger does my EV need simplifies planning. Adapters can expand the use of fast EV charging, giving drivers access to multiple networks. By following standards and using the right adapters, you reduce charging issues while maintaining efficiency and battery health.
Considerations for Home Charging vs Public Charging Networks
Home charging with a Level 1 EV charger or Level 2 EV charger is often simple and largely compatible across vehicles, demonstrating why many ask Are EV chargers universal. Home units adhere to EV charging standards, allowing multiple brands to plug in safely. Public EV charging infrastructure, however, varies widely. EV charging station types range from Level 2 units to DC fast charging systems. Drivers need to check EV plug types and may require an EV adapter for charging. Questions like Can I use any charger for my EV arise because public networks include multiple standards, including CHAdeMO connector, CCS charging standard, and proprietary systems like Tesla NACS port.
Home charging emphasizes convenience and electric car charging speed suitable for daily needs. Public networks demand awareness of fast EV charging availability and electric car fast charger locations. Using an EV charging compatibility chart helps prevent mismatches. Knowledge of EV charging in different countries is crucial for travelers. Comparing Tesla charging vs other EVs clarifies network limitations. Observing EV charging safety standards ensures safe operations. Understanding AC vs DC EV charging allows drivers to select the correct system. Proper planning helps answer Do all electric cars use the same charger and ensures reliable charging everywhere.
What EV Owners Should Check Before Assuming Compatibility
Before plugging in, every EV owner should evaluate EV charger compatibility to answer Are EV chargers universal accurately. Checking EV charging port type and connector ensures correct fit. Awareness of EV plug types like CHAdeMO connector, CCS charging standard, or Tesla NACS port avoids costly errors. An EV adapter for charging may solve mismatches, but users should confirm fast EV charging capabilities first. Checking EV charging standards, EV charging infrastructure, and using an EV charging compatibility chart guarantees safe operation. Questions like Can I use any charger for my EV or Do all electric cars use the same charger require this preparation.
Owners should also review electric car charging speed, EV charging station types, and EV charging safety standards. Awareness of AC vs DC EV charging helps prevent overloading. For international use, understanding EV charging in different countries ensures global compatibility. Knowledge of Level 1 EV charger, Level 2 EV charger, and DC fast charging types prevents unexpected delays. Checking What type of charger does my EV need and Universal EV charger myths ensures realistic expectations. Proper preparation allows efficient charging while protecting battery health and vehicle electronics.
Future Trends Towards Greater Standardisation in EV Charging
The EV industry is moving toward more EV charging standards to answer Are EV chargers universal. Initiatives to unify EV plug types and promote Universal EV plug adoption are underway. Collaboration between manufacturers may reduce reliance on proprietary systems like Tesla NACS port or CHAdeMO connector. Fast EV charging is expected to become more accessible with standardized DC stations. Increased EV charging infrastructure ensures public networks provide multiple EV charging station types for all brands. Awareness of EV adapter for charging may still be necessary in transitional periods.
Future improvements will also affect electric car charging speed, AC vs DC EV charging, and global compatibility. Efforts to simplify EV charging in different countries will help international travelers. Standardization benefits users choosing the Best EV charger for multiple brands, and makes EV charging safety standards easier to follow. Tools like EV charging compatibility chart and knowledge of EV connector types explained will guide safe and efficient use. Standardization promises broader access, fewer adapters, and faster, reliable charging for all EV drivers.
Implications for Countries Like Pakistan or Emerging Markets
Emerging markets face unique challenges with EV charger compatibility, impacting whether Are EV chargers universal applies locally. Infrastructure is limited, so access to Level 2 EV charger or DC fast charging stations may be scarce. EV charging infrastructure is still developing, and public networks often offer few EV charging station types. Drivers need to check EV plug types and consider EV adapter for charging to ensure vehicles can connect safely. Awareness of EV charging in different countries is essential for imported vehicles.
Local adoption affects electric car charging speed and access to fast EV charging. Knowledge of EV charging standards, EV charging safety standards, and EV connector types explained helps prevent problems. Home setups with EV home charger remain the most practical solution. Drivers must check What type of charger does my EV need and review EV charging compatibility chart before installation. Understanding AC vs DC EV charging and proprietary connectors like Tesla NACS port ensures vehicles charge efficiently. Proper planning addresses concerns like Can I use any charger for my EV in developing regions.
Can You Rely on a “Universal” EV Charger?
While a true Universal EV plug is a long-term goal, current reality shows Are EV chargers universal is mostly false for fast and international charging. Level 1 EV charger and most Level 2 EV charger units are broadly compatible, but DC fast charging, proprietary connectors like Tesla NACS port, CHAdeMO connector, and CCS charging standard create exceptions. Drivers asking Do all electric cars use the same charger need to check EV charger types, EV charging standards, and EV charging infrastructure. EV adapter for charging and EV charging compatibility chart remain essential tools for compatibility.
Understanding electric car charging speed, fast EV charging, EV connector types explained, and EV charging safety standards ensures safe and effective operation. Knowledge of EV charging in different countries, EV charging station types, and AC vs DC EV charging prepares drivers for travel and everyday use. Considering What type of charger does my EV need and Universal EV charger myths provides realistic expectations. While universality is limited, awareness, proper adapters, and planning allow drivers to charge efficiently, safely, and confidently in any scenario.
FAQ’s
Are electric vehicle chargers universal across all brands?
Electric vehicle chargers are not fully universal. While Level 1 and Level 2 chargers work with most vehicles, DC fast chargers and proprietary connectors like Tesla NACS port or CHAdeMO require adapters or brand-specific stations. Understanding EV charger compatibility ensures safe and efficient charging.
Can I use any charger for my EV at home or public stations?
At home, most EVs support Level 1 or Level 2 charging safely. In public, compatibility varies due to connector types such as CCS or CHAdeMO. Using an EV adapter for charging and checking an EV charging compatibility chart prevents misuse and ensures correct electric car charging speed.
What are the main connector types and their compatibility?
Major connector types include J1772, Type 2, CHAdeMO, CCS, and Tesla NACS port. Each follows specific EV charging standards, impacting fast EV charging options. Knowing EV plug types and regional differences is essential for both home and public charging setups.
Why are DC fast chargers not universal?
DC fast chargers supply high voltage directly to the battery, requiring standardized communication protocols. Proprietary systems like Tesla NACS port or CHAdeMO prevent universal use. Awareness of fast EV charging specifications and EV charging safety standards ensures efficient and safe operation.
How can EV owners ensure compatibility when traveling internationally?
International travelers must check EV charging in different countries for local connectors and voltage standards. Carrying an EV adapter for charging and consulting an EV charging compatibility chart allows use of both public and home chargers safely across regions.
Conclusion
Ultimately, are electric vehicle chargers universal remains a nuanced question. While standard Level 1 EV charger and Level 2 EV charger systems offer broad compatibility, fast charging and proprietary connectors limit full universality. Knowing EV connector types explained and following EV charging standards ensures vehicles charge safely and efficiently. For international travel or public networks, using an EV adapter for charging and referencing EV charging compatibility charts helps maintain consistent performance. Understanding these distinctions allows EV owners to plan effectively, avoid errors, and achieve optimal electric car charging speed across diverse charging environments.