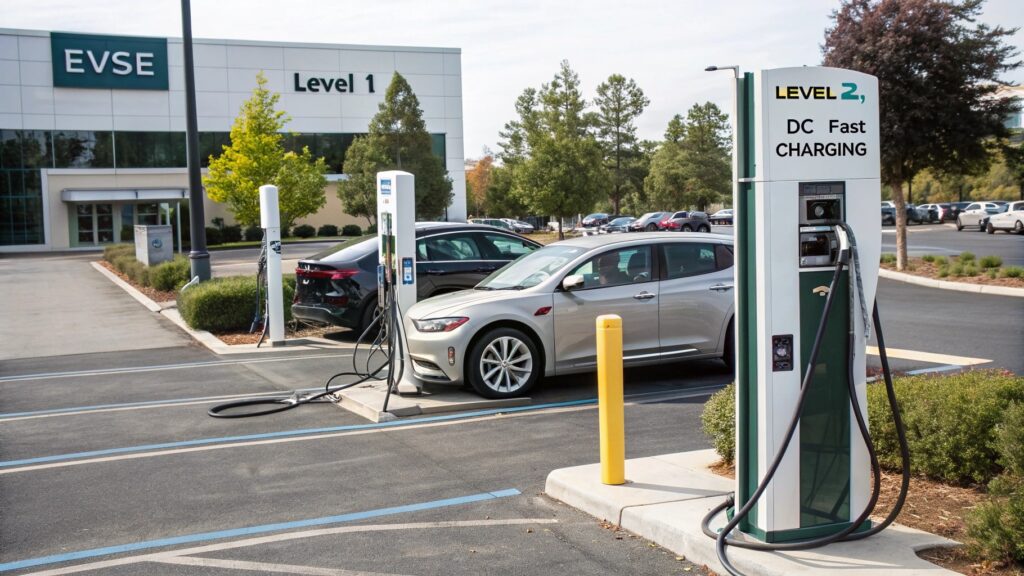
The answer to “Are all electric vehicle chargers the same” is no. Variations in EVSE types, EV plug types, and charging speed influence compatibility and performance. Understanding EV charging standards and the differences between Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers and DC fast charging empowers drivers to make informed choices. Proper knowledge ensures efficient home setups, seamless use of EV public charging stations, and optimized travel planning. By considering voltage, power, and connector type, EV owners can enjoy safe, reliable, and cost-effective charging tailored to their precise car and lifestyle.
What “electric vehicle charger” actually means
An electric vehicle charger is the device that supplies electricity to your car’s battery so it can run. Many drivers wonder, What types of EV chargers exist? The solution is varied. Different cars require different charging methods depending on battery size, voltage, and connector. Some chargers are simple and slow, while others, like DC fast charging, provide rapid power. EVSE types define the standard equipment for EV charging, and understanding them helps you avoid mistakes. EV plug types and the EV charger plug standard also play crucial roles, as they dictate which car can physically connect. Can I use any charger for my EV? Not always. Chargers vary in voltage, amperage, and connectors. Knowledge of EV connector types ensures compatibility. Overall, knowing what an EV charger is and how it works is vital for all drivers seeking safe, fast, and reliable charging options.
Electric vehicle chargers are more than just cords and plugs. They vary in electric car charging types and the power they supply. Home EV charger installation often requires planning, as many homes cannot support high-power chargers without upgrades. EV public charging stations offer convenience, but different networks might not accept all vehicles. Drivers often ask, Do all EV chargers fit all cars? Understanding AC vs DC chargers and Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers is critical. Chargers also differ by compatibility with brand-specific technologies, like Tesla supercharger compatibility, which is limited to certain models unless adapters are used. EV charging standards provide a framework for safety and interoperability, but regional differences exist. Whether you use a fast charging network or a standard charger, knowing these details ensures your car charges Efficiently, safely, and with out damage.
The three main charging levels Level 1, Level 2 & DC fast charging
Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers define the first distinction in EV charging. Level 1 chargers use standard household outlets, provide slow energy flow, and are ideal for overnight charging at home. Level 2 chargers operate at higher voltage, delivering faster charging and supporting larger batteries. Many drivers wonder, What is the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 chargers? It comes down to speed, cost, and practicality. DC fast charging is another level entirely, offering rapid energy transfer and is mostly found at public stations. It allows drivers to recharge up to 80% in less than an hour. Understanding EV charging speed comparison across these levels helps drivers plan trips and manage downtime efficiently.
DC fast charging also introduces a higher power requirement that only certain EVSE types support. EV plug types differ between DC fast and AC Level 1 or Level 2 chargers. Are DC fast chargers better than AC? They are faster, but cost more and put more stress on the battery over time. EV charging standards ensure that each level is safe and compatible with vehicle design. Chargers also vary by brand; for example, Tesla supercharger compatibility is not universal without adapters. Considering your driving habits and battery size helps determine which level to prioritize. A combination of home and public charging is usually the most convenient and economical approach for most EV owners.
Charging plug & connector types explained (J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, NACS)
EV connector types are crucial to know before choosing a charger. Common connectors include J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, and NACS. Drivers often ask, Which plug type does my EV use? Compatibility depends on the vehicle make and region. For example, Japanese EVs may use CHAdeMO, while European and American cars favor CCS. Can I use a Tesla charger for other EVs? Only with proper adapters. EV charger plug standard varies globally, and the wrong connection can prevent charging or even damage the battery. Chargers also differ in voltage and amperage output, making plug choice a key factor.
Connector types affect how quickly the vehicle charges. DC fast charging often requires a specialized plug, while Level 2 chargers use more standardized connectors like J1772. EV plug types also determine whether home EV charger installation is straightforward or requires additional adapters. Charging at EV public charging stations may require different plugs depending on the network. Understanding CHAdeMO vs CCS allows EV owners to plan trips efficiently. Safety and speed depend on using the correct connector. Drivers benefit from checking EV charging standards before purchasing chargers or visiting public stations.
Regional and country differences in EV charging standards
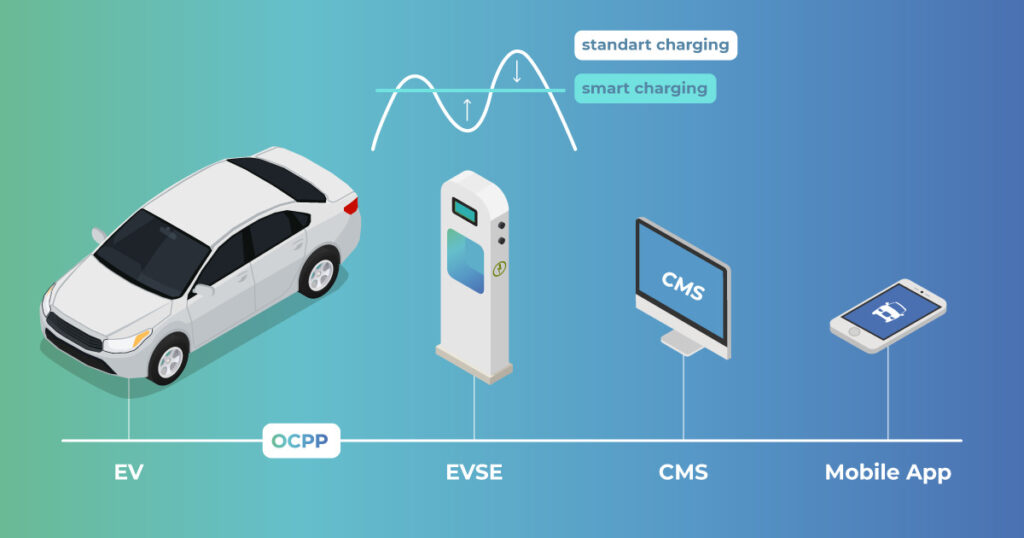
EV charging standards differ by country, affecting EVSE types and plug compatibility. In the U.S., J1772 is common for AC, while CCS is favored for DC fast charging. Europe uses Type 2 and CCS Combo 2, while Japan prefers CHAdeMO. Drivers often ask, Which EV chargers are compatible worldwide? Standardization efforts are underway, but differences remain. EV charging speed comparison varies by region, as infrastructure affects output. Voltage differences also influence electric car charging types, with 120V outlets slower than 240V equivalents.
These regional differences impact travel planning. EV public charging stations may not have every connector, requiring adapters. Tesla supercharger compatibility also varies by country, with some networks using local plug standards. Understanding EV charging standards helps drivers avoid incompatibility and delays. Costs also differ, with electric car charging cost fluctuating based on local electricity rates. Awareness of these variations ensures that drivers maintain reliable, safe charging wherever they travel.
How compatibility between charger and vehicle works
Do all electric powered vehicles use the equal charger?No, compatibility depends on plug type, voltage, and software. Vehicles are designed for specific EV plug types and power levels. Adapters can bridge gaps, but safety protocols must be followed. Charging adapter for EV allows some cross-brand charging, but not every charger is suitable. EVSE types and connector choices influence whether Level 1, Level 2, or DC fast charging can occur safely.
Compatibility is influenced by brand restrictions. Tesla supercharger compatibility is limited without special adapters. EV charging standards ensure that chargers and cars communicate properly to prevent overcharging. Drivers should confirm plug type, maximum amperage, and charger certification. Home EV charger installation must also align with the vehicle’s capacity. Understanding how compatibility works prevents damage, enhances efficiency, and guarantees reliable charging across home and public stations.
Why charging speed, voltage & power matter
How speedy do EV chargers charge?Speed depends on voltage and power output. Higher voltage allows more energy to flow to the battery. Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers illustrate this difference, with Level 2 charging faster due to higher voltage. DC fast charging offers even more power, reducing downtime significantly. EV charging speed comparison helps drivers plan routes and manage energy needs.
Voltage and power also affect battery health. AC vs DC chargers impact longevity differently, with frequent DC fast charging potentially stressing the battery. Understanding EV charging standards ensures safe energy transfer. Charger quality and compatibility with EV plug types also matter. Optimal charging balances speed, safety, and efficiency, helping drivers enjoy convenience without compromising battery life.
Home vs public charging how the context changes things
Home EV charging station setups provide convenience but may require electrical upgrades. How to put in an EV charger at home? Professional set up guarantees protection and efficiency.EV charger installation cost varies by power level, wiring needs, and equipment quality. Home charging is slower, but accessible, and allows overnight charging without public fees.
EV public charging stations are faster and support DC fast charging, ideal for road trips. Fast charging network membership may provide added benefits but requires compatible plugs. Public stations may not support all EV connector types, and costs differ based on speed. EVSE types and EV charging standards dictate performance. Understanding context ensures drivers choose the right combination of home and public chargers for convenience and efficiency.
Can you use any charger for any car? (compatibility myths & facts)

Can I use any charger for my EV? Not always. Plug type, power output, and voltage dictate compatibility. Many believe all chargers are universal, but EV connector types and proprietary systems like Tesla supercharger compatibility prove otherwise. Adapters exist but must meet EV charging standards for safety.
Myths about universal chargers can lead to inefficiency or battery stress. EVSE types and EV plug types matter. Level 1 and Level 2 chargers provide flexibility, but DC fast charging requires proper connectors. Understanding these facts ensures optimal charging speed, battery health, and safe operation. Knowledge of EV charging speed comparison and connector types prevents surprises during travel or installation.
Brand‑specific networks and proprietary connectors (e.g., the case)
Certain brands maintain proprietary networks. Tesla supercharger compatibility is limited to Tesla models unless adapters are used. Proprietary systems often offer faster speeds, integration with apps, and optimized charging curves. Other manufacturers like Nissan or BMW may also provide brand-specific stations. EV plug types differ across these networks, impacting access.
Travel planning requires understanding brand limitations. Fast charging network membership may influence charging access. EVSE types vary, and EV charging standards ensure safety across systems. Adapters can expand access, but each connector carries voltage and power limits. Knowing brand-specific differences helps drivers avoid downtime and select the most convenient charger for each journey.
Installation & infrastructure considerations (home wiring, public grid)
How to put in an EV charger at home? Installation depends on home wiring, breaker capacity, and local codes. EV charger installation cost may include labor, parts, and upgrades. Level 2 chargers often need 240V outlets, while AC vs DC chargers differ for public grids. Infrastructure affects charging speed and safety.
Public grid connections also matter. EV public charging stations rely on utility power and may limit output during peak hours. EVSE types must meet EV charging standards to prevent surges. Understanding electrical requirements helps drivers install compatible chargers at home or select public stations efficiently. Proper installation ensures reliable, safe, and fast charging.
Cost implications charger types, install costs, electricity costs
Electric car charging cost depends on power level, local electricity rates, and installation. EV charger installation cost includes hardware, labor, and permits. Level 1 chargers are cheapest to install but slow, while Level 2 and DC fast charging are expensive yet faster.
Ongoing costs vary. Home EV charger installation allows controlled electricity rates, while EV public charging stations may charge premium prices. Choosing the right EV plug types and understanding EVSE types affects efficiency. Knowledge of cost implications guides drivers in balancing convenience, speed, and budget.
Future trends standardisation, faster charging, vehicle‑to‑grid
EV era evolves rapidly.. Standardization efforts aim to unify EV charging standards, EV connector types, and EVSE types globally. Faster charging technology reduces wait times, and vehicle-to-grid systems enable cars to supply energy back to the grid.
EV charging speed comparison improves with innovation. Tesla supercharger compatibility and universal adapters may expand access. Emerging electric car charging types like ultra-fast DC chargers promise convenience. Drivers who stay informed on trends can make smarter choices, ensure compatibility, and take advantage of new infrastructure efficiently.
How to choose the right charger for your EV and driving habits
How to choose the right EV charger? Consider battery size, travel patterns, and EV charging speed comparison. Home chargers are convenient, while fast charging network access is critical for long trips. EV plug types and EVSE types ensure compatibility.
Charging needs depend on daily use. Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers affect overnight charging, and DC fast charging benefits long-distance travel. Understanding EV connector types and EV charging standards ensures safe, efficient, and reliable performance. Proper selection balances speed, cost, and convenience.
Common misconceptions about EV chargers
Why are EV chargers different? Many believe all chargers work with all cars, but variations in EV plug types, voltage, and EVSE types prove otherwise. Do all electric powered vehicles use the equal charger? No, compatibility is brand, region, and model dependent.
Other myths include assuming DC chargers are always better or that adapters can overcome all differences. EV charging speed comparison, CHAdeMO vs CCS, and Tesla supercharger compatibility clarify misunderstandings. Knowing the facts improves efficiency, safety, and travel planning.
Key take‑aways & practical advice for EV drivers
Are all home EV chargers the same? No. Home, public, AC, DC, and fast chargers all differ. Understanding EV charging types, EV connector types, and EVSE types is essential. Drivers must consider speed, compatibility, and infrastructure when selecting chargers.
Check EV charging standards and EV plug types before installation. Combine home EV charger installation with public networks for flexibility. Knowing electric car charging cost, EV charging speed comparison, and regional differences ensures safe, efficient, and convenient charging. Proper knowledge helps EV owners save time, reduce cost, and extend battery life.
FAQ’s About Are All Electric Vehicle Chargers the Same
What makes electric vehicle chargers different from each other?
Electric vehicle chargers vary in voltage, amperage, and connector type, which directly affects charging speed and compatibility. Differences in EVSE types, Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers, and DC fast charging capabilities determine which vehicles they can safely service.
Can I use any charger for my EV?
Not all chargers are universally compatible. Vehicle-specific EV connector types and proprietary networks like Tesla supercharger compatibility require correct plugs or adapters to ensure safe and efficient charging.
What are the main EV charging levels and their differences?
Level 1 chargers use standard outlets for slow home charging, Level 2 chargers provide faster AC charging at higher voltage, and DC fast charging delivers rapid energy transfer at public stations, optimizing convenience for long-distance travel.
How do regional standards affect EV charger compatibility?
Different regions follow distinct EV charging standards, including connector types like CHAdeMO vs CCS, voltage levels, and power outputs. Understanding these variations is essential for seamless home and public charging across countries.
What should I consider when choosing the right EV charger?
Evaluate daily driving needs, battery size, desired charging speed, and compatibility with EV plug types and EVSE types. Balance electric car charging cost, infrastructure availability, and brand-specific networks to ensure efficiency, safety, and convenience.
Conclusion
In summary, the answer to “Are all electric vehicle chargers the same” is no. Variations in EVSE types, EV plug types, and charging speed influence compatibility and performance. Understanding EV charging standards and the differences between Level 1 vs Level 2 chargers and DC fast charging empowers drivers to make informed choices. Proper knowledge ensures efficient home setups, seamless use of EV public charging stations, and optimized travel planning. By considering voltage, power, and connector type, EV owners can enjoy safe, reliable, and cost-effective charging tailored to their precise car and lifestyle.