Exploring Do Electric Cars Have Alternators clarifies a key difference between traditional engines and electric drivetrains. Electric vehicles eliminate alternators because they use DC-to-DC converters and regenerative braking systems to efficiently power 12-volt components. This shift reduces moving parts, enhances energy recovery, and minimizes maintenance. So, when someone asks if electric cars have alternators, the answer highlights technological evolution. EVs are designed for smarter, cleaner, and more efficient power management. As the EV electrical subsystem design continues to advance, it’s evident that alternators belong to the past, replaced by intelligent energy conversion systems.
Why EVs Don’t Use Traditional Alternators
Electric vehicles don’t use traditional alternators because they lack engines that produce mechanical motion. A typical alternator in a gasoline car converts engine power into electrical energy for accessories. In EVs, the main battery already stores high-voltage electricity, eliminating the need for this device.
Instead, EVs employ a power conversion inside an electric car system that provides low-voltage current to run essential systems like lights, infotainment, and sensors.The EV electrical subsystem design ensures that energy is efficiently distributed without wasting power. This streamlined architecture means fewer moving parts, less maintenance, and more reliability. So, when asking why don’t electric vehicles use alternators, the answer lies in design efficiency and direct electrical energy management.
What Replaces the Alternator in Electric Cars
In electric cars, the alternator’s role is replaced by a DC to DC converter in EVs. This converter draws energy from the main high-voltage traction battery and transforms it into 12 volts to power smaller systems. It ensures stability for components that require lower voltage levels.
The electric car auxiliary power supply depends entirely on this converter to maintain steady performance. It acts as a lifeline for systems like power steering, air conditioning, and vehicle electronics. Thus, when people ask what replaces the alternator in an electric car, the simple answer is a high-efficiency DC-to-DC converter. This electronic device makes sure that low voltage battery EV systems are constantly charged and functional, even when the car isn’t running.
How a DC-to-DC Converter Works in EVs
A DC to DC converter in electric vehicles serves as a smart intermediary between the main battery and the 12-volt battery. It steps down the voltage from hundreds of volts to just twelve, supplying consistent current to auxiliary systems.
Unlike mechanical alternators, this converter operates silently and without friction. It’s an integral part of EV engineering electrical design principles, helping to optimize performance and reduce energy loss. When discussing how does the DC to DC converter works in electric vehicles, it’s essential to know that it automatically manages charging flow, protecting both batteries from overloading. This design ensures that accessories remain active, even when the EV isn’t in motion.
Key Differences Between Alternators and EV DC-to-DC Converters
| Feature / Function | Traditional Alternator (Gas Vehicles) | DC-to-DC Converter (Electric Vehicles) |
| Power Source | Driven by engine belt and mechanical motion | Draws energy from high-voltage traction battery |
| Primary Purpose | Generates electricity to recharge 12-volt battery and power accessories | Converts high-voltage DC to 12V DC for vehicle systems |
| Efficiency | Limited by mechanical and friction losses | Highly efficient electronic energy conversion |
| Moving Parts | Contains rotors, belts, and bearings | No moving parts – fully electronic |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic replacement or belt adjustments | Minimal maintenance – fewer wear components |
| Operation Sound | Produces mechanical noise | Operates silently |
| Energy Recovery | None – depends solely on engine rotation | Works alongside regenerative braking for energy recovery |
| Use in Vehicles | Found in gasoline and diesel vehicles | Used in all modern battery electric vehicles (BEVs) |
| Reliability | Can fail due to wear or heat | Long lifespan, stable under variable loads |
Role of Regenerative Braking in Charging the 12-Volt System
Regenerative braking system EV technology recovers energy during deceleration, feeding it back into the main battery. Some of this energy indirectly powers the 12-volt system through the converter. This innovation replaces the alternator’s energy generation function found in gas vehicles.
When the driver applies brakes, the EV motor as generator concept captures kinetic energy, turning it into usable electricity. This process enhances electrical energy recovery in EVs, improving efficiency. So, can regenerative braking replace an alternator in EVs? Yes, in a way it complements the DC-to-DC converter’s work, ensuring continuous power for essential systems.
Why Alternators Worked for Gas Cars but Not EVs
Traditional vehicles used alternators because their engines produced rotational motion. This motion turned belts that spun the alternator, creating electricity. Electric cars don’t have combustion engines, making alternators unnecessary.
The EV electrical subsystem design relies on stored battery energy rather than mechanical motion. In contrast, gas vehicles required constant mechanical generation. This explains why electric cars have no traditional engine driven alternator. EVs instead focus on power conversion inside electric car systems that are far more efficient and adaptable for modern driving needs.
Do Hybrids Have Alternators Compared to Full EVs
When comparing whether a hybrid car has an alternator compared to full EV, the answer varies. Hybrids often still use small alternators because they retain internal combustion engines. These engines provide mechanical rotation that can generate electricity.
However, hybrid vs full electric alternator systems show clear differences. Full electric vehicles eliminate mechanical alternators entirely, depending on converters for voltage management. Hybrids sit in between the two technologies, slowly moving toward complete electric systems. This design distinction highlights the evolving EV component battery management system role in energy regulation and storage.
How EV Electrical Systems Maintain 12-Volt Power Without an Engine
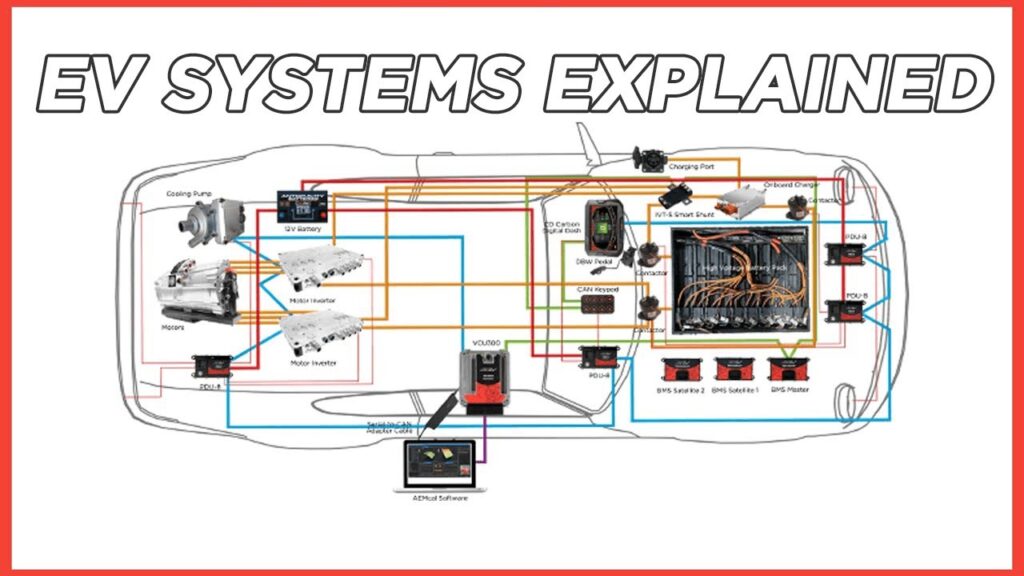
Electric cars maintain 12-volt power using a DC to DC converter in EVs instead of an engine-driven alternator. This converter automatically activates when the main battery is charged or in use.
It provides energy to the auxiliary electrical load in EVs, powering everything from the lights to the cabin electronics. The EV service and maintenance power module also ensures that backup systems are stable. So, how does the electric car electrical system maintain auxiliary loads? Through precise power flow regulation that never depends on mechanical parts, making EVs more dependable and quieter.
Differences in Power Architecture Between Internal Combustion & Electric Vehicles
The automotive electrical architecture of electric vehicles differs completely from gas-powered designs. In combustion cars, power originates from the alternator and engine cycle. In EVs, it flows from the traction battery through converters and inverters.
A power conversion inside an electric car system ensures voltage consistency for all circuits. The EV charging system vs power management integrates seamlessly, maintaining energy across multiple functions. When people ask what is the difference between EV auxiliary architecture vs ICE car, the distinction is clear EVs rely on electronic transformation rather than mechanical motion.
Common Misconceptions Are EVs Trying to Generate Power While Driving?
Many believe electric cars try to generate power while moving, but that’s not accurate. Unlike alternators, EVs use regenerative braking system EV technology to recover energy only during deceleration, not continuous driving.
This principle prevents unnecessary drag and energy waste. The electrical energy recovery in EVs happens strategically, ensuring balance between battery preservation and range efficiency. So, do EVs ever need mechanical generators like alternators? No, because they already have integrated systems for energy conversion that outperform traditional designs.
How Tesla Manages Its Auxiliary Electrical Load
Tesla uses an advanced EV electrical subsystem design that integrates inverter and converter components in EVs for efficient load management. Its 12-volt systems are maintained by a compact DC-to-DC converter, not an alternator.
According to Tesla’s design reports, this system optimizes the EV motor as a generator concept and supports high reliability. The electric car auxiliary power supply ensures uninterrupted operation of lights, sensors, and controls. This illustrates how all electric cars share the same auxiliary power design, but Tesla’s model shows how smart converters replace alternators with precision electronics.
Why Alternators Would Be Less Ideal in EVs
Alternators require belts, pulleys, and mechanical contact points, all potential failure sources. In EVs, the EV engineering electrical design principles aim for fewer moving parts and more electronic reliability.
A DC to DC converter in EVs ensures safer operation under controlled voltage. This eliminates overheating and mechanical wear. That’s why an alternator is needed in battery electric vehicles. Safety, efficiency, and durability are far superior with converter-based systems, making alternators obsolete in EV design.
Why EV Designers Avoid Mechanical Generators
The EV service and maintenance power module is largely software-controlled, unlike alternators that need regular physical maintenance. Fewer components mean lower upkeep costs and better long-term reliability.
Because of this, do electric cars require alternator replacement like gas cars? No. Their electronic converters last much longer and rarely fail. The electric vehicle power architecture emphasizes longevity and smooth operation through smart circuitry rather than mechanical wear parts.
How EV Charging & Battery Management Systems Handle Auxiliary Loads
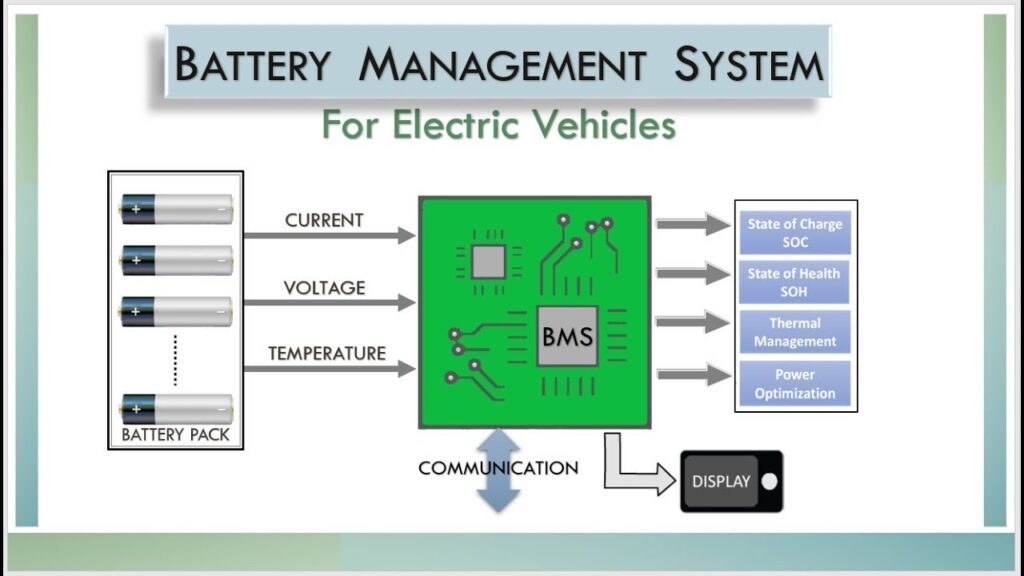
EVs depend on the EV component battery management system role to balance voltage between the main and auxiliary batteries. This ensures that how an EV charges its 12 volt battery is controlled digitally.
The system coordinates between charging stations and onboard converters, managing EV charging system vs power management seamlessly. Whether driving or parked, these systems regulate current flow precisely to maintain power stability and protect circuits from overcharging or draining.
Future Innovations Could EVs Ever Use Alternator-Like Generators?
Future technologies may explore compact EV motors as generator concept solutions that mimic alternators electronically. These would generate energy without moving parts, improving recovery efficiency.
However, most engineers agree that the reasons EVs do not have alternators remain valid weight, efficiency, and system simplicity. While innovations in EV charging future standards continue, traditional alternators will likely never return to electric cars due to their mechanical limitations.
What You Need to Know as an EV Owner About Your Low-Voltage System
As an EV owner, it’s essential to understand your low voltage battery EV systems and how converters support them. Regularly checking the health of your auxiliary battery ensures smooth function for lights and electronics.
If issues occur, it might signal a DC to DC converter malfunction, not an alternator failure. This shows what happens if a DC to DC converter fails in an EV, accessories may lose power, but the main drive battery remains unaffected. Knowing this helps drivers make informed maintenance decisions.
FAQ’s
Do electric cars have alternators like traditional vehicles?
No, electric cars do not have alternators. They use a DC-to-DC converter that draws energy from the main battery to power 12-volt systems instead of relying on an engine-driven alternator.
What replaces the alternator in electric cars?
In electric vehicles, the alternator is replaced by a DC-to-DC converter that steps down high-voltage battery power to 12 volts for lights, infotainment, and other auxiliary systems.
Why don’t electric vehicles need alternators?
Electric vehicles don’t need alternators because they lack combustion engines. Their main traction battery already supplies electrical energy, managed efficiently by converters and battery management systems.
How does the 12-volt battery stay charged in an electric car?
A DC-to-DC converter continuously recharges the 12-volt battery using energy from the main battery pack, ensuring all low-voltage components remain operational.
Can regenerative braking replace an alternator in EVs?
Regenerative braking doesn’t replace the alternator directly but complements the system by recovering kinetic energy, which helps recharge the main battery and supports efficient power management
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring does electric cars have alternators clarifies a key difference between traditional engines and electric drivetrains. Electric vehicles eliminate alternators because they use DC-to-DC converters and regenerative braking systems to efficiently power 12-volt components. This shift reduces moving parts, enhances energy recovery, and minimizes maintenance. So, when someone asks if electric cars have alternators, the answer highlights technological evolution. EVs are designed for smarter, cleaner, and more efficient power management. As the EV electrical subsystem design continues to advance, it’s evident that alternators belong to the past, replaced by intelligent energy conversion systems.